Overview Of Front-end Development
Exploring the Core Aspects and Components of Front-end Development
Introduction
In the vast realm of the internet, the web experienced a remarkable transformation, evolving beyond its humble beginnings. Our journey through the digital landscape unfolded across various versions:
Web1: The Static Era In the early days, Web1 brought forth static pages served directly from the server's file system. This was an era of limited user-to-server communication, where personal web pages found their home on ISP (Internet Service Provider)-run servers or free hosting services.
Web2: The Interactive Wave With the advent of Web 2, user interaction took centre stage. We witnessed the introduction of web applications, ushering in an era of dynamic content. User-generated content, video streaming, and online collaboration became the norm, marking the rise of social media dialogue.
Web3: The Decentralized Frontier Web3 emerged as a paradigm shift where users gained newfound control. Reading, writing, and owning content became pivotal. Data opened its doors to transparency, and the concept of a decentralised web took root, challenging the traditional structures.
Web5: Empowering the User As the digital saga evolved, Web5 embraced the concept of a truly decentralised web, placing users at the helm. This era celebrated a user-centric approach where individuals wielded authority over their data, symbolising a powerful shift in the web's narrative.
Amidst these transformations, the division of web development into frontend and backend became essential. The increasing complexity of websites demanded specialised skills for different parts of their development. As websites evolved to include dynamic content and interactive features, the need arose to separate presentation (frontend) from data management and server-side logic (backend). This division allowed developers to specialise, fostering more efficient development processes and enhancing the overall performance of web applications.
Frontend development is like the cover of your favourite magazine. Imagine walking past a newsstand and spotting a magazine that catches your eye. You don't need to read every magazine to know if it's worth buying; the captivating cover art, vibrant colours, and bold headlines draw you in immediately. It's love at first sight!
Similarly, front-end development focuses on creating the visual and interactive elements of a website or web application that grab users' attention and make them want to explore further. Like a well-designed magazine cover, a well-executed front end can leave a lasting impression and keep users returning for more. We often refer to the front end as the client side, where users interact directly with their web browsers. It includes elements such as the user interface (UI), design, layout, and functionality that users see and interact with.
Front-end Technologies
Frontend technology refers to the collection of tools, programming languages, frameworks, and libraries used to build the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of a web application. It encompasses everything that users interact with directly in their web browsers, including layout, design, content, and functionality.
Let's dive into the key technologies needed to build the front end of web applications.
HyperText Markup Language (HTML)
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is the code that structures web pages. It is comparable to the skeleton of a body because it contains all of the many components that make up a web page, including inputs, headings, paragraphs, and graphics. Every online application has a purpose and meaning because of HTML.
HTML Code looks like this 👇
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>First Project</title>
</head>
<body>
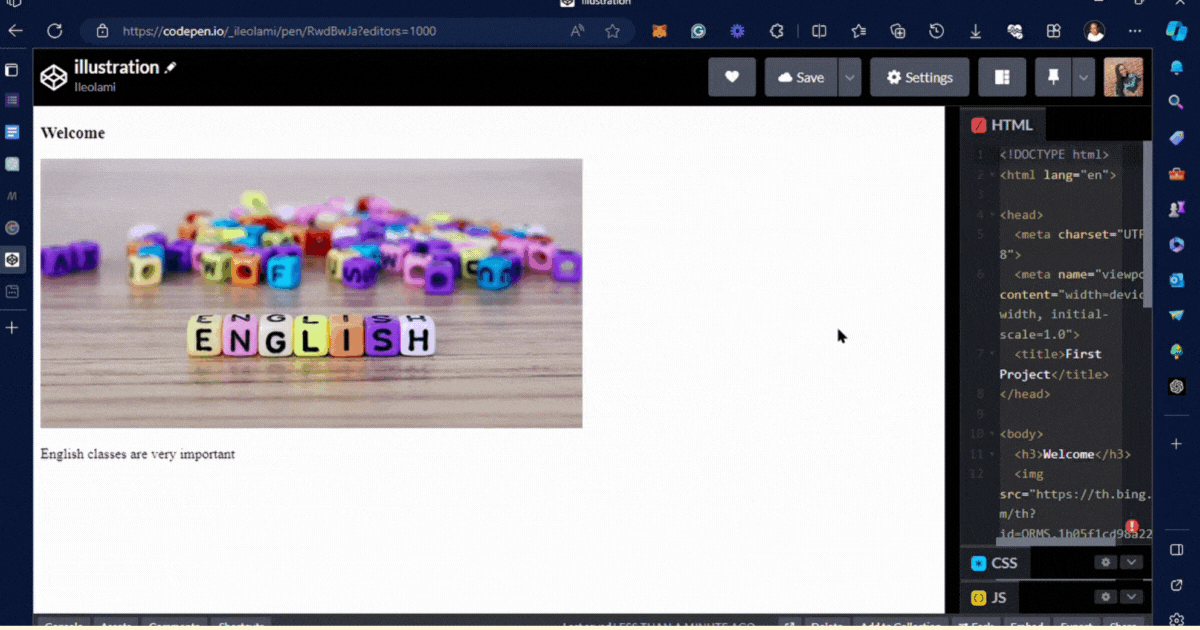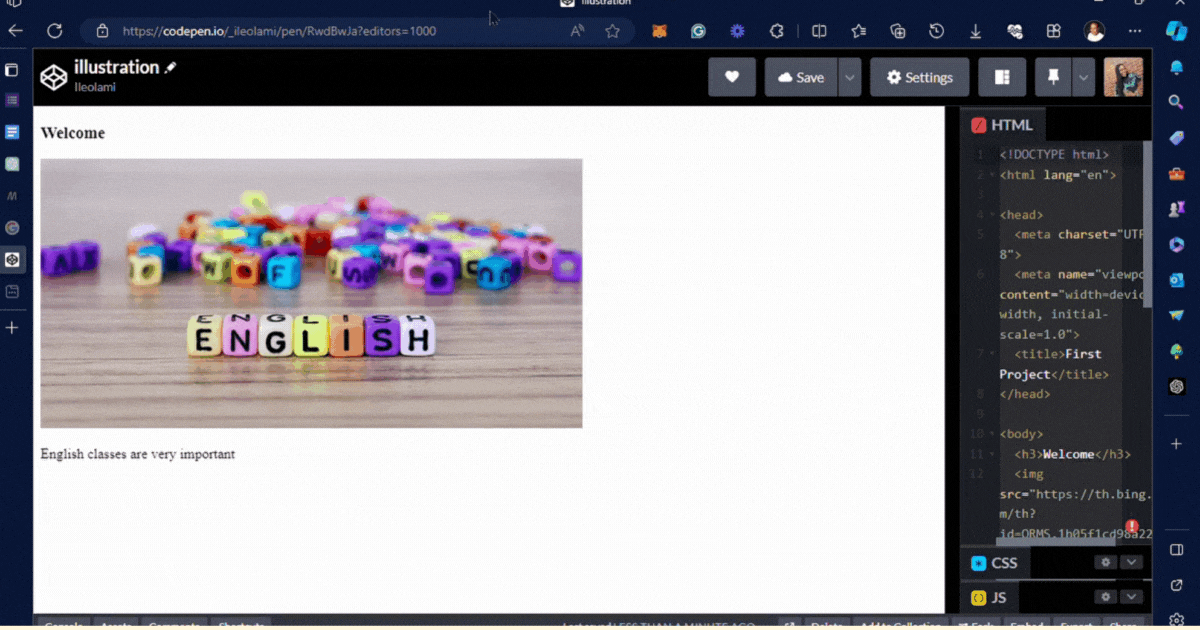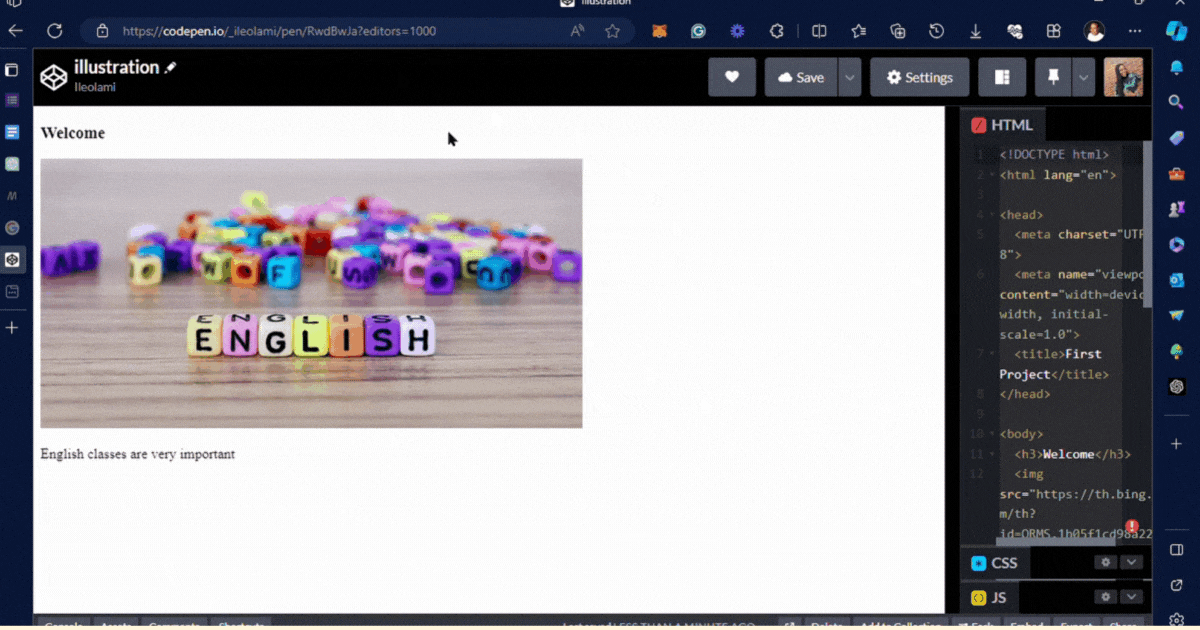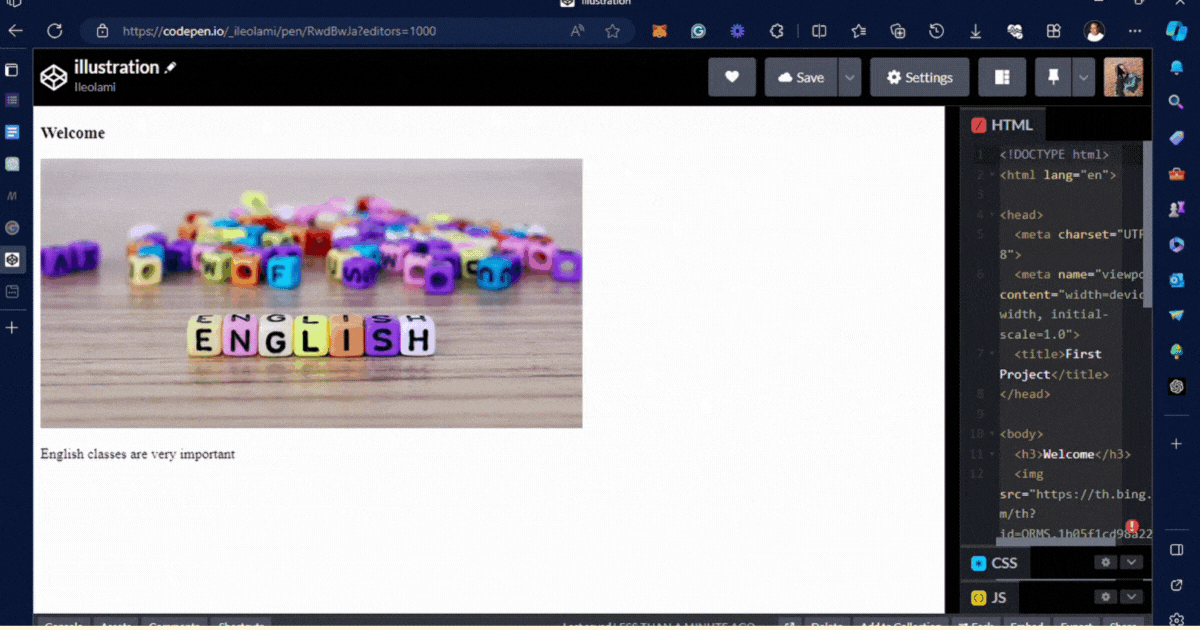
<h3>Welcome</h3>
<img src="https://th.bing.com/th?id=ORMS.1b05f1cd98a22ff716ef240b72e03d7a&pid=Wdp&w=612&h=304&qlt=90&c=1&rs=1&dpr=0.8999999761581421&p=0">
<p>English classes are very important</p>
</body>
</html>
output 👇
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
CSS is used to style the HTML elements, including layout, colours, fonts, and other visual aspects of the web page. In short, CSS is used to add beauty to HTML elements.
CSS code looks like this 👇
h3{
font-size: 400%;
color: green;
font-style: italic;
font-weight: 900;
border: 1px solid black;
width: 40%;
border-radius: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
img{
border-radius: 3%;
}
p{
color: red;
font-size : 300%;
}
output 👇

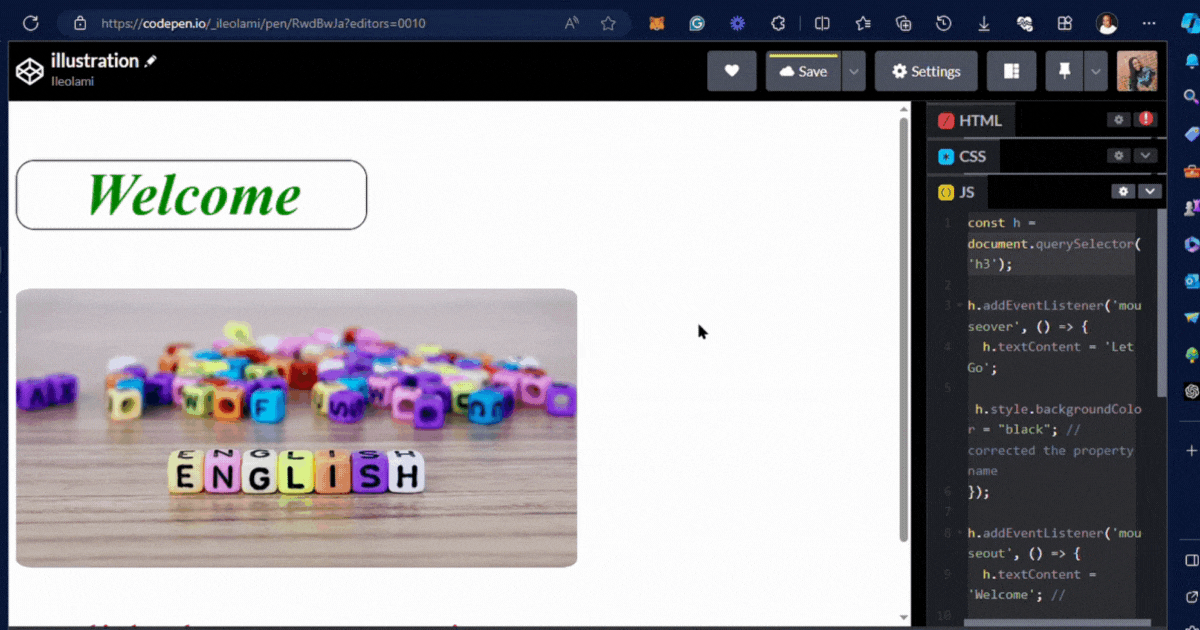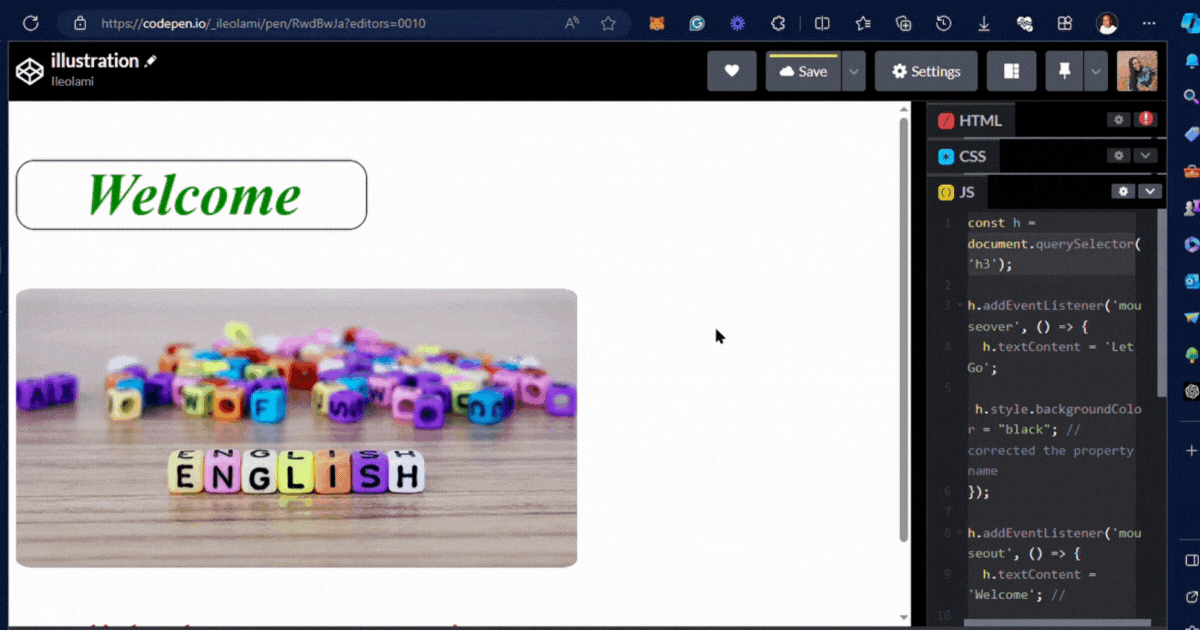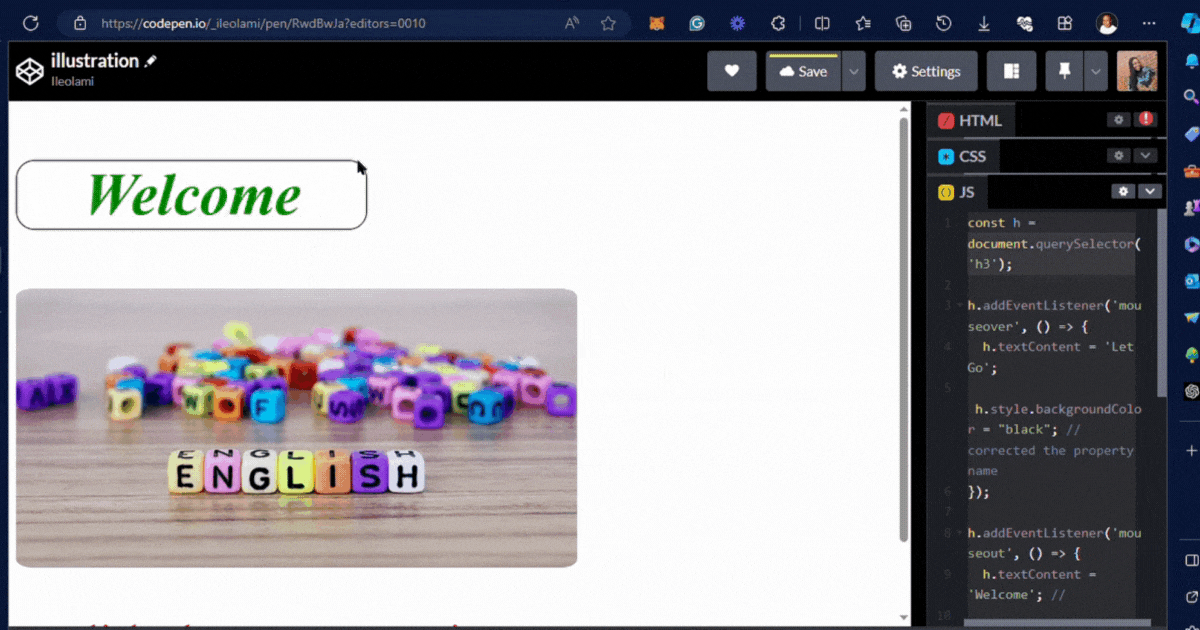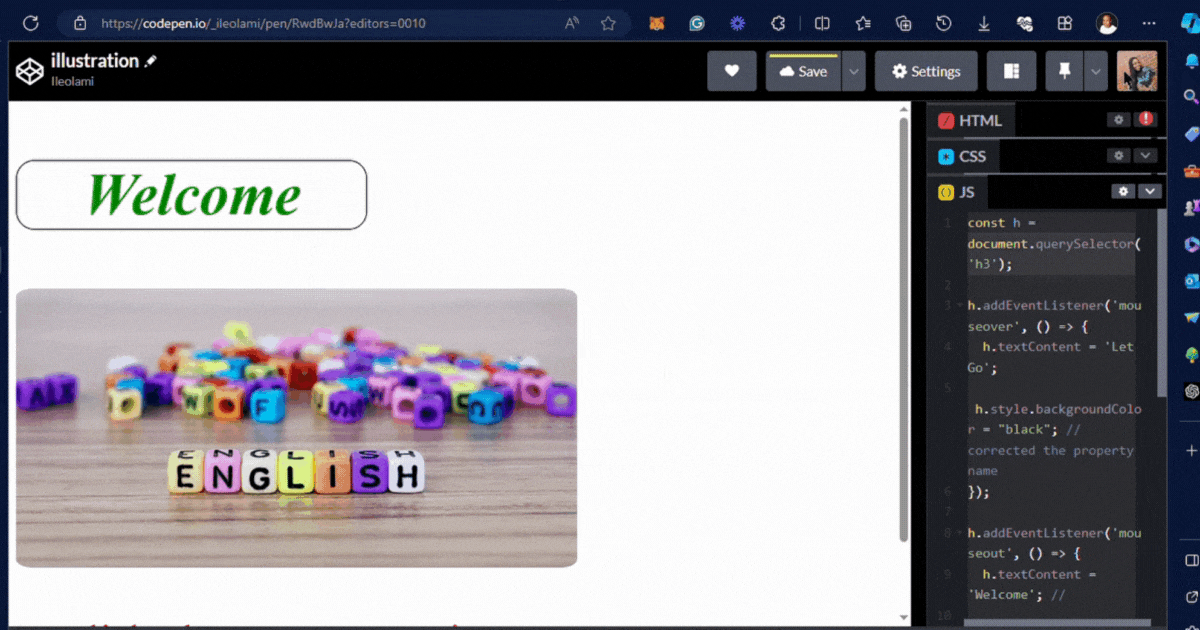
JavaScript(JS)
JavaScript is a programming language that adds functionality and dynamic behaviour to web pages. It is used for tasks such as form validation, DOM manipulation, handling user interactions, etc.
JS looks like this 👇
const h = document.querySelector('h3');
h.addEventListener('mouseover', () => {
h.textContent = 'Let Go';
h.style.backgroundColor = "black";
});
h.addEventListener('mouseout', () => {
h.textContent = 'Welcome'; //
h.style.backgroundColor = "initial";
});
output 👇
Frontend Frameworks/Library
Frontend frameworks and libraries like React, Angular, Next.js, Tailwind.css, and Vue.js provide developers with pre-built components and tools to streamline the development process and build complex web applications more efficiently.
Version Control System
In version control systems like Git, code is tracked to manage changes, facilitate collaboration among team members, and maintain code integrity.
Build Tools
Build tools like Webpack, Vite, and Parcel help automate tasks such as bundling, minification, and code optimisation to improve frontend development workflow and performance.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
APIs allow frontend developers to interact with backend operations and external data sources to access and manipulate data dynamically within web applications.
Key Components of Frontend
To effectively fulfil your role as a front-end developer, it's essential to know the key components that form your responsibilities. A clear understanding of these components not only enhances your performance but also eradicates any potential gaps or uncertainties for your fellow developers.
The foundational components for every front-end application form the pillar of your work. As a front-end developer, keeping these components in mind enables you to develop seamless, visually appealing, and user-friendly web applications.
These components include:
Browser Compatibility
This involves ensuring all web applications work efficiently across various browsers, e.g. Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Brave, etc. Frontend developers should test and apply the necessary fallbacks.
Accessibility
Web accessibility ensures that applications are accessible and usable by people with impairments and comply with accessibility standards and guidelines. Frontend developers can achieve these using semantic HTML, ARIA attributes, keyboard navigation, and other accessibility features to make web content perceivable, operable, and understandable for all users.
Responsive Design
Responsive Design ensures web applications display optimally across all various devices and screen devices including mobile devices.
Perfomance Optimazation
Performance optimization involves improving the load times, rendering speed, and overall responsiveness of a webpage by optimizing frontend code, assets, and resources. Techniques such as minification of code, lazy loading, optimizing images, and caching are utilized to enhance performance.
User Experience (UX) Design
Frontend developers collaborate closely with UX designers to create intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable user experiences. They implement features such as navigation, feedback mechanisms, and accessibility tools.
Conclusion
This article has been able to establish what frontend development entails, the technologies used and the components every frontend developer must know when developing applications.
When seeking front-end developer positions, it's advisable to carefully review the job description to comprehend the specific requirements and expectations associated with the role.
I hope you find this helpful, If you do, let me know in the comment section
like💗, comment ✍ and Follow 🏃♀️or

